FROGS Core

Galaxy
- Get Started ▾
- Reads processing
- Remove chimera
- Cluster/ASV filters
- Taxonomic affiliation
- Phylogenetic tree building
- ITSx
- Read demultiplexing
- Affiliatio filters
- Affiliation postprocessing
- Abundance normalisation
- Convert Biom file to TSV file
- Convert TSV file to Biom file
- Cluster/ASV report
- Affiliation report
Main tools
Optional tools
CLI
- Get Started
- Reads processing
- Remove chimera
- Cluster/ASV filters
- Taxonomic affiliation
- Phylogenetic tree building
- ITSx
- Read demultiplexing
- Affiliation filters
- Affiliation postprocessing
- Abundance normalisation
- Convert Biom file to TSV file
- Convert TSV file to Biom file
- Cluster/ASV report
- Affiliation report
Main tools
Optional tools
Taxonomic affiliation
Context
The taxonomic affiliation tool from the FROGS pipeline is designed to assign taxonomy to the seed sequence of each ASV (Amplicon Sequence Variant).
It integrates external tools such as RDPtools and BLAST to provide robust and reliable taxonomic annotations. These annotations are then added to the
BIOM file and can be summarized into an HTML report for visualization. This step is essential to link the ASV sequences obtained after clustering and
chimera removal to their potential biological identity, making downstream ecological and microbiome analyses possible.
How it does
The tool requires three main inputs: a reference database (pre-formatted and BLAST-indexed FASTA), a BIOM file containing ASV abundance data, and a
FASTA file of ASV seed sequences.
It then performs taxonomic assignment using either BLAST alignment against the reference database or the RDP classifier (if specified).
Depending on the configuration, it can store a single taxonomy, a consensus taxonomy, or a list of possible taxonomies, along with optional metadata
such as bootstrap values, alignment identity, and coverage.
The output consists of a new BIOM file enriched with taxonomic affiliations, an HTML report with graphical summaries of the taxonomy distribution,
and a log file documenting the commands executed. These results provide a structured and reproducible way to connect ASVs to their taxonomic classification.
Configuration: 16S V3V4 Swarm
It is now time to give our clusters a taxonomic affiliation. We use the most up-to-date available version of Silva (v.138.1) among all databanks available in the dedicated repository:
/save/user/frogs/galaxy_databanks/SILVA/16S . In this tutorial, we are using the Silva pintail 100 database, but this is to keep the database small. It may not be the most suitable database for your data.
sbatch -J affiliation -o LOGS/affiliation.out -e LOGS/affiliation.err -c 8 --export=ALL --wrap="module load devel/Miniforge/Miniforge3 && module load bioinfo/FROGS/FROGS-v5.0.2 && taxonomic_affiliation.py --input-fasta FROGS/SWARM/filters.fasta --input-biom FROGS/SWARM/filters.biom --nb-cpus 8 --log-file FROGS/SWARM/affiliation.log --output-biom FROGS/SWARM/affiliation.biom --html FROGS/SWARM/affiliation.html --reference /save/user/frogs/galaxy_databanks/SILVA/16S/silva_138.1_16S_pintail100/silva_138.1_16S_pintail100.fasta && module unload bioinfo/FROGS/FROGS-v5.0.2"
taxonomic_affiliation.py --help)
Interpretation: 16S V3V4 Swarm
This report shows that all clusters were affiliated.
You can use the Krona output to explore the affiliation.
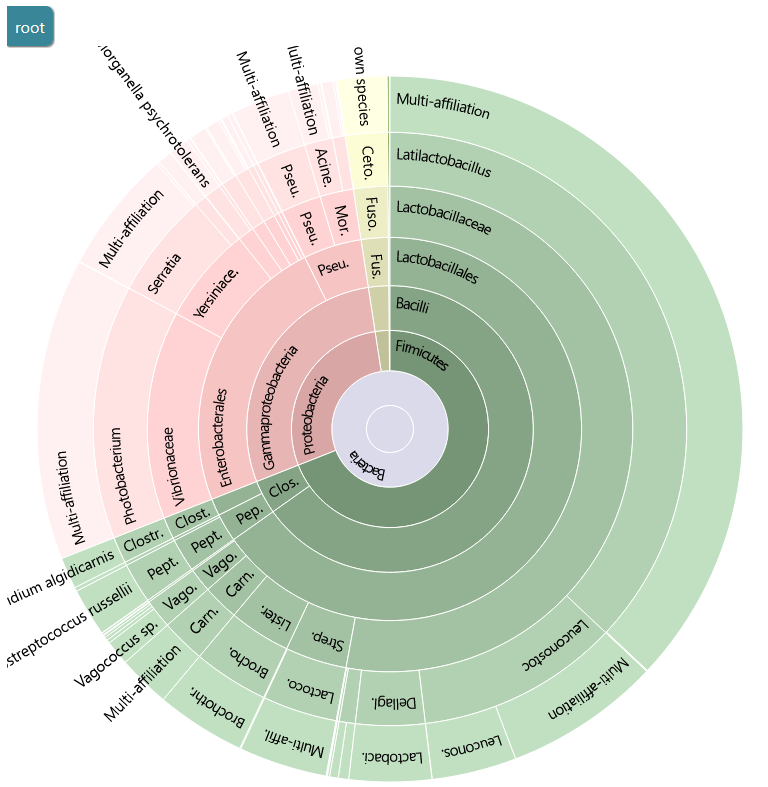
You can use the Krona output to explore the affiliation.

