FROGS Core

Galaxy
- Get Started ▾
- Reads processing
- Remove chimera
- Cluster/ASV filters
- Taxonomic affiliation
- Phylogenetic tree building
- ITSx
- Read demultiplexing
- Affiliatio filters
- Affiliation postprocessing
- Abundance normalisation
- Convert Biom file to TSV file
- Convert TSV file to Biom file
- Cluster/ASV report
- Affiliation report
Main tools
Optional tools
CLI
- Get Started
- Reads processing
- Remove chimera
- Cluster/ASV filters
- Taxonomic affiliation
- Phylogenetic tree building
- ITSx
- Read demultiplexing
- Affiliation filters
- Affiliation postprocessing
- Abundance normalisation
- Convert Biom file to TSV file
- Convert TSV file to Biom file
- Cluster/ASV report
- Affiliation report
Main tools
Optional tools
Remove chimera
Context
Chimeras are artifact sequences formed by two or more biological sequences incorrectly joined together.
This often occurs during PCR reactions using mixed templates (i.e., uncultured environmental samples).
Incomplete extensions during PCR allow subsequent PCR cycles to use a partially extended strand to bind
to the template of a different, but similar, sequence. This partially extended strand then acts as a
primer to extend and form a chimeric sequence. Once created, the chimeric sequence is then further
amplified in subsequent cycles. The end result is a PCR artifact that does not represent a sequence
that exists in nature. This phenomena is particularly common in amplicon sequencing where closely
related sequences are amplified.
How it does
This tool removes chimeric sequences by sample.
De novo detection: In this algorithm, a chimera-free reference database is automatically generated for each NGS data. Initially, the reference database is empty. Then, NGS reads are considered in the order of decreasing abundance. If a sequence is classified as chimeric, it is discarded; otherwise, it is added to the reference database (so the size of the reference database grows). Candidate parents (PCR templates, strains A and B in the previous figure) are required to have more abundance than that of the query sequence, on the assumption that a chimera has undergone fewer rounds of amplification and will, therefore, be less abundant than its parents (Edgar et al., 2011).
The chimera detection is performed with VSEARCH combined with a homemade strategy. The chimera detection is performed sample by sample and a cross-validation is performed to remove only chimera identified in all samples where they are present.
De novo detection: In this algorithm, a chimera-free reference database is automatically generated for each NGS data. Initially, the reference database is empty. Then, NGS reads are considered in the order of decreasing abundance. If a sequence is classified as chimeric, it is discarded; otherwise, it is added to the reference database (so the size of the reference database grows). Candidate parents (PCR templates, strains A and B in the previous figure) are required to have more abundance than that of the query sequence, on the assumption that a chimera has undergone fewer rounds of amplification and will, therefore, be less abundant than its parents (Edgar et al., 2011).
The chimera detection is performed with VSEARCH combined with a homemade strategy. The chimera detection is performed sample by sample and a cross-validation is performed to remove only chimera identified in all samples where they are present.
Configuration: Short reads (16S V3V4 use cases)
The chimera detection is performed with vsearch.
mkdir FROGS/SWARM/
sbatch -J chimera -o LOGS/chimera.out -e LOGS/chimera.err -c 8 --export=ALL --wrap="module load devel/Miniforge/Miniforge3 && module load bioinfo/FROGS/FROGS-v5.0.2 && remove_chimera.py --input-fasta FROGS/denoising_swarm.fasta --input-biom FROGS/denoising_swarm.biom --output-fasta FROGS/SWARM/remove_chimera.fasta --nb-cpus 8 --log-file FROGS/SWARM/remove_chimera.log --output-biom FROGS/SWARM/remove_chimera.biom --html FROGS/SWARM/remove_chimera.html && module unload bioinfo/FROGS/FROGS-v5.0.2"
remove_chimera.py --help)
Interpretation: Short reads (16S V3V4 use cases)
Let look at the HTML file to see the result of remove chimera.
You have three panels: Summary, Cluster distribution, and Sample distribution. Here, we will focus primarily on the Summary panel.

Since the Clusters distribution and Samples distribution panels are common to multiple tools, a more detailed interpretation with vizualisation of these panels can be found in the Cluster Stat section .
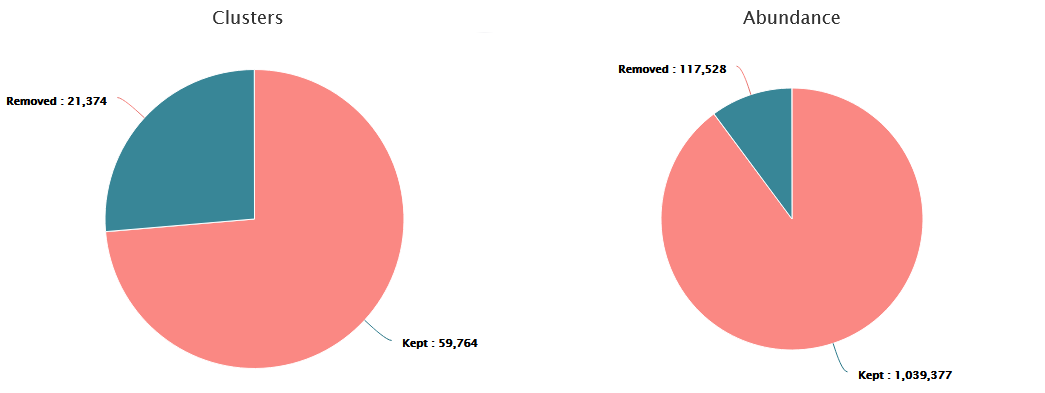
These graphs illustrate the number of chimeric clusters and sequences.
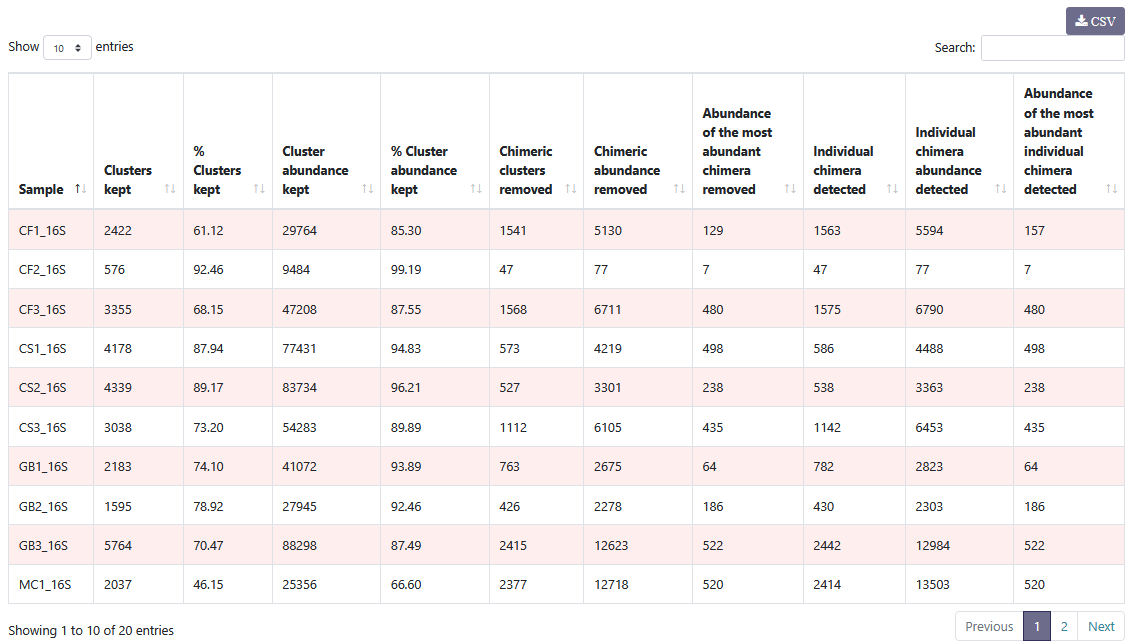
You can see details on chimeric clusters and sequences within each sample. You can sort the columns by clicking on .
.
You have three panels: Summary, Cluster distribution, and Sample distribution. Here, we will focus primarily on the Summary panel.

Since the Clusters distribution and Samples distribution panels are common to multiple tools, a more detailed interpretation with vizualisation of these panels can be found in the Cluster Stat section .

These graphs illustrate the number of chimeric clusters and sequences.
- ~10% of sequences (26.3% of clusters) are chimeric
- Chimeric clusters are made of few sequences
Chimera detection by sample

You can see details on chimeric clusters and sequences within each sample. You can sort the columns by clicking on
 .
.
Configuration: Short reads (ITS use cases)
The chimera detection is performed with vsearch.
mkdir FROGS/ITS/
sbatch -J chimera -o LOGS/chimera.out -e LOGS/chimera.err -c 8 --export=ALL --wrap="module load devel/Miniforge/Miniforge3 && module load bioinfo/FROGS/FROGS-v5.0.2 && remove_chimera.py --input-fasta FROGS/denoising_its.fasta --input-biom FROGS/denoising_its.biom --output-fasta FROGS/ITS/remove_chimera.fasta --nb-cpus 8 --log-file FROGS/ITS/remove_chimera.log --output-biom FROGS/ITS/remove_chimera.biom --html FROGS/ITS/remove_chimera.html && module unload bioinfo/FROGS/FROGS-v5.0.2"
remove_chimera.py --help)
Interpretation: Short reads (ITS use cases)
Let look at the HTML file to see the result of remove chimera.
You have three panels: Summary, Cluster distribution, and Sample distribution. Here, we will focus primarily on the Summary panel.

Since the Clusters distribution and Samples distribution panels are common to multiple tools, a more detailed interpretation with vizualisation of these panels can be found in the Cluster Stat section .
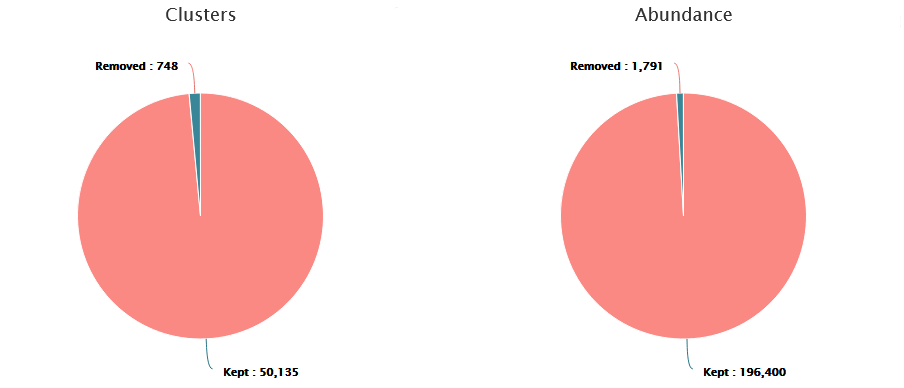
These graphs illustrate the number of chimeric clusters and sequences.
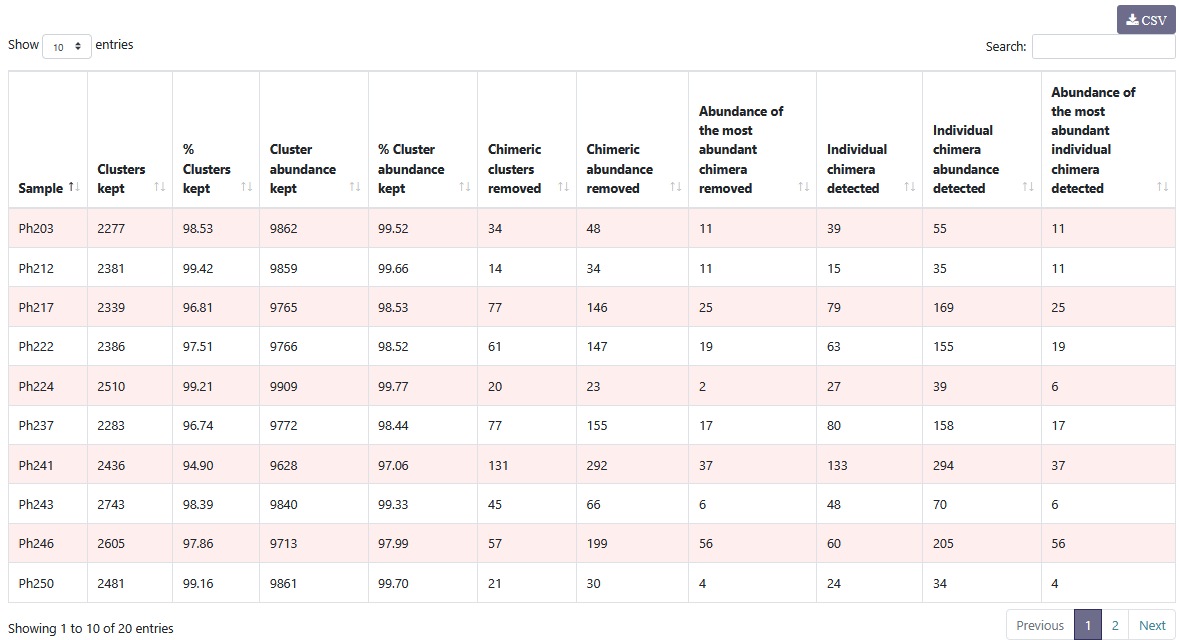
You can see details on chimeric clusters and sequences within each sample. You can sort the columns by clicking on .
.
You have three panels: Summary, Cluster distribution, and Sample distribution. Here, we will focus primarily on the Summary panel.

Since the Clusters distribution and Samples distribution panels are common to multiple tools, a more detailed interpretation with vizualisation of these panels can be found in the Cluster Stat section .

These graphs illustrate the number of chimeric clusters and sequences.
- ~1% of sequences (1.5% of clusters) are chimeric
Chimera detection by sample

You can see details on chimeric clusters and sequences within each sample. You can sort the columns by clicking on
 .
.
